
Code Jumper Curriculum: Lessons, Lesson 9 Constants
American Printing House for the Blind
Code Jumper Curriculum: Lessons
Copyright © 2020 American Printing House for the Blind
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, except as expressly permitted under copyright law, without written permission of the publisher.
Published by American Printing House for the Blind
1839 Frankfort Avenue, Louisville, KY 40206
www.aph.org | [email protected]
Overview
Lesson Objectives
Students will:
- Understand the meaning of a constant when used in a computer program
- Understand that constants are used when the computer program needs to use a specific value
- Be able to develop programs that use constants
Expected Outcomes
Students will:
- All students: Be able to add a constant to an existing program
- Most students: Be able to use a constant to control a loop in a new program
- Some students: Be able to explain what a constant is and how they have used it in their own programs
Lesson Plan Structure
- Unplugged Activity
- Guided Code Jumper Activity
- Exploration
- Standards and Check for Understanding
Resources:
- Code Jumper Tutorial Videos
- Code Jumper App: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vg72YPz6CWY
- The Hub: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KGb51PW9zJQ&lis=
- Play and Pause Pod: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=446jCw8qcDI&t=
- LoopPod: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EFKbKLlD3HI
- Plugs: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hTy8moSohlE
- Code Cards
Key Vocabulary
- Constant: A fixed value that can’t be changed
Unplugged Activity
Objective
After this lesson, students will understand the meaning of something that is constant.
Key Vocabulary
- Citizenship: the behavior expected as a member of a community
- Digital Citizenship: the behavior expected as a member of a digital community
Materials
- Computer Science Journal
- White board or projection from a computer
- Near distance copies available of materials presented at a distance as needed
Instruction
- Divide students into groups of two to four. Ask students to write down the word citizenship in their Computer Science Journals. Brainstorm ideas about what makes a good citizen and encourage students to write it down in their journals.
- Give students five minutes to record all their ideas. Bring the group back together and have each group give ideas. Ask the students to add all the ideas that their group did not come up with to their Computer Science Journals. Ask each group to contribute ideas.
- Ask students to add the word digital next to the word citizenship in their Computer Science Journals. In their small groups, ask students to mark the ideas they brainstormed for citizenship that now also work with digital citizenship. Digital citizenship is the continuously developing norms of appropriate, responsible, and empowered technology use.
- Ask students what word remained constant and at the center of their brainstorm?
- (Answer: citizenship)
- Explain to students that the characteristics of a good citizen are also the characteristics of a good digital citizen and, as a result, citizenship becomes the constant.
Ideas for a good digital citizen†:
- Advocates for equal digital rights and access for all
- Treats others with respect in online spaces and never cyberbullies
- Does not steal or damage others’ digital work, identity, or property
- Makes appropriate decisions when communicating through a variety of digital channels
- Uses digital tools to advance their learning and keeps up with changing technologies
- Makes responsible online purchasing decisions and protects their payment information
- Upholds basic human rights in all digital forums
- Protects personal information from outside forces that might cause harm
- Proactively limits health risks of technology, from physical to psychological
Explain to students that in computer programming, a constant is a value that stays the same.
Closure
Review with students that in this activity, citizenship is the constant. The same values students shared for being a good citizen need to be remembered so they can refer to them later when they are online as digital citizens.
Code Jumper Guided Activity
Lesson Objective
After this lesson, students will be able to develop programs that use constants.
Vocabulary
- Constant: A fixed value that can’t be changed
Materials
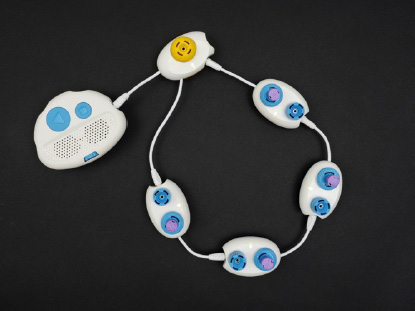
- Code Jumper Kit
- Computer Science Journal
- Constant Code Card 1
- Constant Code Card 2
- Constant Code Card 3
- Constant Code Card 4
- Sound Set Mapping
Instruction
- Read Constant Code Card 1: Make New Friends and create it with your Code Jumper Kit. Set the loop to 1.
- Introduce the concept of a constant. Ask students what the word constant means.
- Explain that a constant is a value that is fixed—that is, a value that cannot be changed.
- Ask students: Where do you see constants every day? Examples are a house number or a telephone number. There are 8 ounces in 1 cup or 1000 milliliters in a liter. Those numbers are constant and never change.
- Play the program “Make New Friends” from Constant Code Card 1.
- Ask students to take out the purple plugs from the Code Jumper Kit and find the plugs that are numbered 1-8. They are all set up like raised dice, with one to eight dots on the top.

[Figure Caption:] Constant plugs 1-8, with raised dots representing each number visible on the top - Insert the plug with two raised dots, or the constant two plug, into the dial on the Loop pod. When a constant is inserted into a loop pod, it overrides the dial. Whatever number that constant represents, it will play the program that number of times. This happens even if you turn the dial on the Loop pod.
Demonstrate this change by playing the program so students can hear “Make New Friends” loop two times.
- Now we will use the Constant plugs to select sounds within a sound set. Each sound in a Sound Set has a specific number attached to it, like a house number. In the Make New Friends Sound Set, the words “Make new friends, but keep the old” plays when constant 1 is inserted into a Play pod. This means that in this sound set, “Make new friends, but keep the old” is the first line in our program to be played. If constant 2 is inserted, “One is silver and the other’s gold” plays because that is the second sound in the sound set, and so on. Demonstrate this by using Constant Code Card 2: Make New Friends with Constants as your guide.


[Figure Caption:] At the top is a screenshot of the Code Jumper app with one thread. Under THREAD 1 Piano, the commands read, LOOP constant(2) times, PLAY C5 for 1/2 a beat, PLAY D5 for 1/2 a beat, PLAY E5 for 1/2 a beat, PLAY C5 for 1/2 a beat, END LOOP; the commands are followed by END THREAD. Below this screenshot are two photos. The photo on the left shows a Code Jumper program with one Play pod and one Constant plug. The Play pod is connected to the Hub at Port 1, and the Constant plug is connected to the port on the Play pod’s Sound dial. The photo on the right, taken from a side angle, shows the Constant plug and Play pod. - Explain that the Constant plug tells the program to ignore the value set on the pod’s Sound dial and will instead use the value on the Constant plug. No matter how many times the dial is turned, it will always play the sound that is associated with the number of the constant.
- Read the code for the program Make New Friends with the Loop pod dial set to 1. To read the code, either press the Play and Stop buttons simultaneously or click the Read button on the app.
- In groups of two to three students per Code Jumper Kit, have students create a program using Play pods and Constant plugs. Distribute the Constant Code Card 3: Mystery Animals to students in the appropriate format.
- Ask students to create the program in Constant Code Card 3: Mystery Animals using the Constant plugs 2, 4, and 7. Ask students to write in their Computer Science Journals the mystery animal they hear, in order. Encourage students to have the code read aloud as they check their work.
Example of how the data can be recorded:
Sound Set:
Play pod Constant Sound 1 4 2 7 3 2 - Ask students to read Constant Code Card 4: Mystery Animals and move the constants to the correct positions. This requires pulling out all the Constant plugs from the program they created and rearranging them. Have students listen to the program and read the code and then record their findings in their Computer Science Journals.
Example of how the data can be recorded:
Sound Set: Animals
Trail 1
Constant Sound Play pod 2 1 4 2 7 3 - Discuss what the differences are between the first and second programs. Ask students: What would you expect if the order was changed to 7, 2, 4?
Example of how the data can be recorded: Sound Set: Animals
Trial 2
Play pod Constant Sound 1 7 2 2 3 4 - Ask students to create a program with at least four Play pods, possibly a Loop pod, and at least three constants.
- Ask students to record their code in their Computer Science Journals.
Closure
- Ask students: What have you noticed when the constants are moved to other Play pods? (The sounds are determined by the constants, so the sound on the Play pod changes.)
- Ask students: What happens when a constant is in the Sound dial and you turn the dial? (The sound does not change. It stays the same.)
- Ask students: What is beneficial about using the plugs? (You know exactly what sound you are going to play. The sounds don’t accidentally get bumped and changed.)
Exploration
Objective
In this exploration, students will create a program using loops, constants, and the Infinity plug.
Vocabulary
- Infinity: Something that never ends
Materials
- Up to eight Play pods
- One loop
- 1-2 threads
- At least three constants
- The Infinity plug
Instruction
- Ask students: Do you know what infinity means? (Expected response: It’s something that never ends.) Explain that in print, the symbol for infinity is often represented by a figure that looks like the numeral 8 in a horizontal position.
- Ask the students to find the Infinity plug from the Code Jumper Kit. Discuss that the Infinity plug is used in the Loop pod to make the loop continue until the Stop button is pressed.
- Give students access to the constants mapping document to help them determine what sounds they would like to use without having to turn the dials for each Play pod or quickly choose the correct Constant plug.
- After discussing the setup requirements, have students create this program by first mapping it out in their Computer Science Journals. All Sound Sets will work for this activity. This can be a basic program and should include where they would like to use the plugs.
- Ask students to create their program, trace the program as it runs, and match it to the code that they wrote in their Computer Science Journals.
Closure
Ask students to reflect on how using Constants and the Infinity plug makes creating code more efficient.
Standards and Check for Understanding
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards*
- 1B-AP-08: Compare and refine multiple algorithms for the same task and determine which is the most appropriate.
National Curriculum of England**:
Key Stage 1:
- Understand what algorithms are, how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions
- Create and debug simple programs
- Use logical reasoning to predict the behavior of simple programs
- Use technology purposefully to create, organize, store, manipulate and retrieve digital content
- Recognize common uses of information technology beyond school
- Use technology safely and respectfully, keeping personal information private; identify where to go for help and support when they have concerns about content or contact on the internet or other online technologies
Key Stage 2:
- Design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts
- Use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output
- Use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs
- Use search technologies effectively, appreciate how results are selected and ranked, and be discerning in evaluating digital content
- Use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognize acceptable/unacceptable behavior; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact.
Closing Activities and Check for Understanding
Ask students to think of examples of values in the real world that are fixed and don’t change. An example is the number of minutes in an hour.
| Check for Understanding | Completed |
|---|---|
| Student understand that a constant is a set value. | Yes / No |
Constant Lesson Code Cards
Teacher Code Cards for Constant Guided Lesson:
Constant Code Card 1: Make New Friends with Loop
- Sample program set up and run by the teacher: Make New Friends
- Sound category: Sample Sounds
- Sound Set: Make New Friends
Thread 1 Make New Friends
LOOP constant(1) times
PLAY Make new friends but keep the old for 1 times speed
PLAY A circle is round, it has no end for 1 times speed
PLAY One is silver and the other’s gold for 1 times speed
PLAY That’s how long I want to be your friend for 1 times speed
END LOOP
End Thread
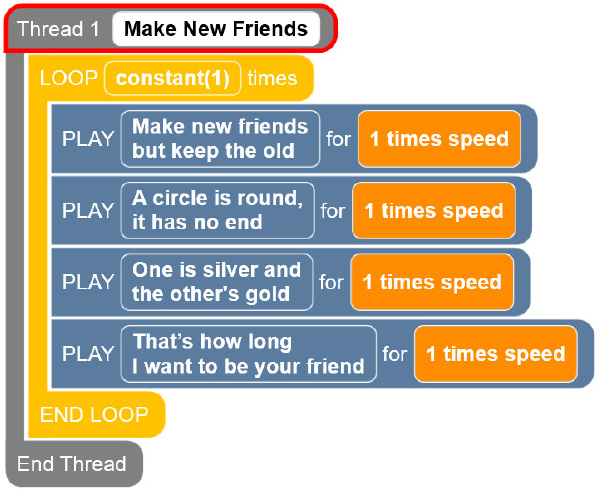


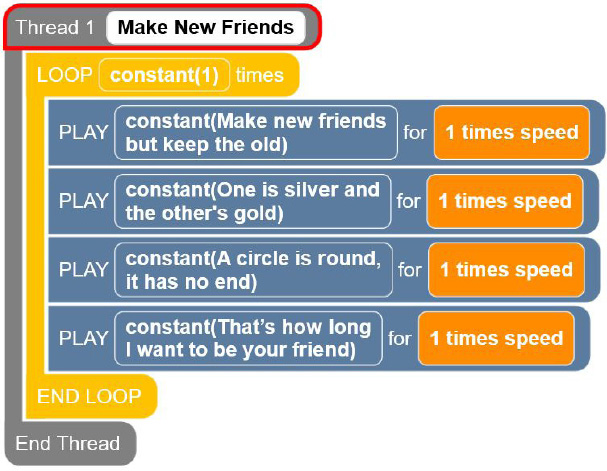
Constant Code Card 2: Make New Friends with Constants
- Sound category: Sample Sounds
- Sound Set: Make New Friends
THREAD 1 Make New Friends
LOOP constant (1) times
PLAY constant (Make new friends but keep the old) for 1 times speed
PLAY constant (One is silver and the other’s gold) for 1 times speed
PLAY constant (A Circle is round, it has no end) for 1 times speed
PLAY constant (That’s how long I want to be your friend) for 1 times speed
END LOOP
END THREAD

Student Code Cards for Constant Guided Lesson:
Constant Code Card 3: Mystery Animals
THREAD 1 Animals
PLAY constant(4)
PLAY constant(7)
PLAY constant(2)
END THREAD
Constant Code Card 4: Mystery Animals
THREAD 1 Animals
PLAY constant(2)
PLAY constant(4)
PLAY constant(7)
END THREAD

For more resources, visit codejumper.com
Copyright © 2020

1839 Frankfort Avenue
Louisville, Kentucky 40206
502-895-2405 • 800-223-1839